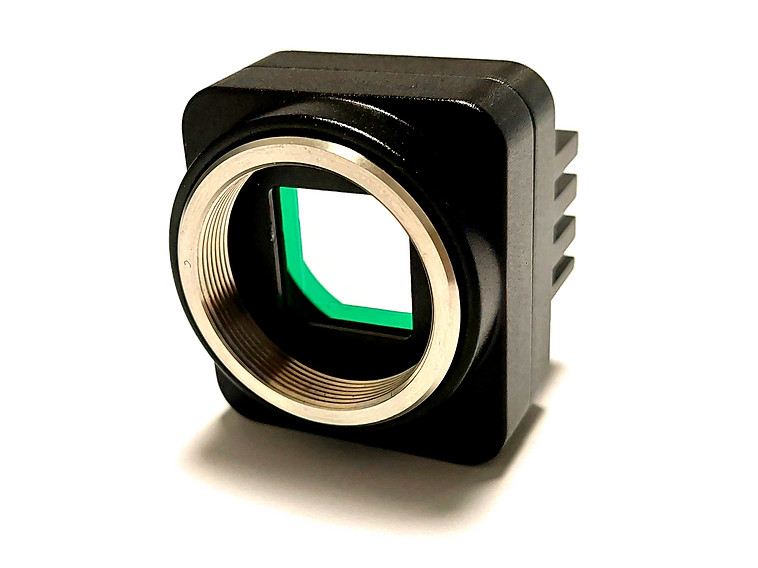
SWIR Multispectral Cameras
SWIR Multispectral Imaging
SWIR multispectral imaging involves capturing image data across multiple discrete wavelengths within the short-wave infrared (SWIR) spectrum, typically ranging from 0.9 to 1.7 micrometers (µm), and in some extended applications, from 0.7 to 2.5 µm. Unlike thermal imaging, which relies on emitted heat, SWIR multispectral imaging is based on reflected infrared light, similar to how visible light imaging works. This makes it especially effective for detecting surface and subsurface features that remain hidden in standard visible or thermal images.
By leveraging unique spectral signatures of materials in the SWIR range, this imaging technique allows for precise material differentiation, quality assessment, and enhanced visibility in challenging environments such as fog, smoke, or low light.
How It Works
At the core of SWIR multispectral imaging are advanced sensors and optical components designed to capture reflected light across selected spectral bands. Cameras designed for this purpose typically use InGaAs (Indium Gallium Arsenide) sensors, which are highly sensitive in the SWIR range.
Modern SWIR systems may also incorporate on-pixel filter technologies, including custom Bayer-like mosaic filters, enabling simultaneous capture of multiple SWIR bands. These filters enable pixel-level spectral differentiation, allowing for real-time imaging without the need for external filters or scanning mechanisms.
This approach delivers high-contrast, high-resolution imagery, which is critical for tasks like:
-
Identifying material composition
-
Visualizing moisture content
-
Penetrating packaging or coatings
-
Detecting defects or contaminants
-
Observing biological or agricultural conditions
Applications of SWIR Multispectral Imaging
SWIR multispectral imaging is a versatile technology used across industries where material composition and visual clarity are essential. Common applications include:
-
Industrial inspection: Detecting hidden defects in semiconductors, solar panels, or composite materials.
-
Agriculture: Monitoring crop health, water stress, or pest damage through spectral analysis.
-
Pharmaceuticals & food processing: Verifying product quality and integrity without damaging packaging.
-
Environmental monitoring: Identifying vegetation stress, pollution, or heat-absorbing surfaces.
-
Defense & surveillance: Seeing through camouflage, fog, or nighttime environments for better situational awareness.
The ability of SWIR multispectral imaging to see through certain materials (such as silicon, plastic, or glass) and reveal features invisible to the human eye makes it a game-changing tool in both commercial and scientific domains.
Why Choose SWIR Multispectral Imaging?
-
Non-destructive and contactless: SWIR imaging allows for inspection without touching or altering the object.
-
Enhanced visibility in harsh conditions: Effective even in smoky, dusty, or dim environments.
-
Precise material identification: Materials exhibit unique reflectance patterns in the SWIR spectrum.
-
Compact and scalable: Newer technologies are enabling portable and integrated multispectral SWIR cameras.